Types of Mental Illness
Mental illnesses can be broadly categorized into several types, each with its own set of symptoms and diagnostic criteria. Some of the most common types of mental illness include:
1. Mood Disorders
Mood disorders, such as depression and bipolar disorder, are characterized by significant changes in mood, energy levels, and daily functioning. Symptoms may include persistent sadness, irritability, changes in sleep and appetite, and difficulty concentrating.
2. Anxiety Disorders
Anxiety disorders involve excessive fear, worry, and nervousness that interfere with daily life. Examples include generalized anxiety disorder, panic disorder, social anxiety disorder, and specific phobias.
3. Psychotic Disorders
Psychotic disorders, such as schizophrenia, are characterized by a disconnection from reality. Symptoms may include hallucinations, delusions, disorganized thinking, and unusual behaviors.
4. Eating Disorders
Eating disorders, such as anorexia nervosa and bulimia nervosa, involve abnormal eating habits and distorted body image. These conditions can have serious physical and psychological consequences.
5. Substance Use Disorders
Substance use disorders involve the persistent use of drugs or alcohol despite negative consequences. These disorders can lead to physical dependence, withdrawal symptoms, and impaired functioning in various aspects of life.
6. Personality Disorders
Personality disorders are characterized by rigid and unhealthy patterns of thinking, behaving, and relating to others. Examples include borderline personality disorder, narcissistic personality disorder, and obsessive-compulsive personality disorder.
It’s important to note that individuals can experience symptoms of multiple types of mental illness simultaneously, a condition known as comorbidity. Accurate mental illness diagnosis is essential for developing an effective mental illness treatment plan that addresses all relevant symptoms and conditions.
Risk Factors for Mental Illness

Mental illnesses can affect anyone, regardless of age, gender, ethnicity, or socioeconomic status. However, certain factors can increase the risk of developing a mental health condition, including:
- Genetics and family history
- Trauma and adverse life experiences
- Chronic medical conditions
- Substance abuse
- Social isolation and lack of support
Understanding these risk factors can help individuals and healthcare providers identify potential mental health concerns early and implement preventive strategies.
The Impact of Mental Illness
Mental illnesses can have a profound impact on various aspects of an individual’s life, as well as on their loved ones and society as a whole. Some of the potential consequences of untreated mental illness include:
- Impaired daily functioning and quality of life
- Strained relationships and social isolation
- Decreased academic or occupational performance
- Increased risk of physical health problems
- Substance abuse and addiction
- Suicidal thoughts and behaviors
Recognizing the far-reaching impact of mental illness underscores the importance of early intervention and effective mental health treatment.
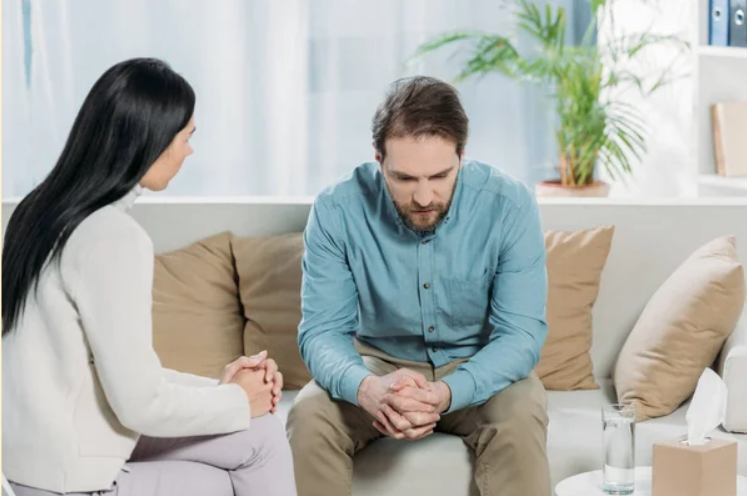
Treatment Options for Mental Illness
Mental illness treatment varies depending on the specific condition, its severity, and the individual’s preferences. A comprehensive treatment plan often involves a combination of approaches, such as:
1. Psychotherapy
Psychotherapy, also known as talk therapy, is a cornerstone of mental health treatment. It involves working with a therapist to address emotional, behavioral, and interpersonal challenges. Some common types of psychotherapy include:
- Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT)
- Dialectical behavior therapy (DBT)
- Interpersonal therapy (IPT)
- Psychodynamic therapy
2. Medication
Psychiatric medications can be an effective tool in managing symptoms of mental illness. Commonly prescribed mental illness treatments include:
- Antidepressants
- Anti-anxiety medications
- Mood stabilizers
- Antipsychotics
It’s essential to work closely with a psychiatrist or other qualified prescriber to find the right medication and dosage, as well as to monitor for potential side effects.
3. Lifestyle Changes
Making healthy lifestyle changes can significantly impact mental well-being. Some beneficial practices include:
- Regular exercise
- Balanced nutrition
- Sufficient sleep
- Stress management techniques
- Mindfulness and relaxation practices
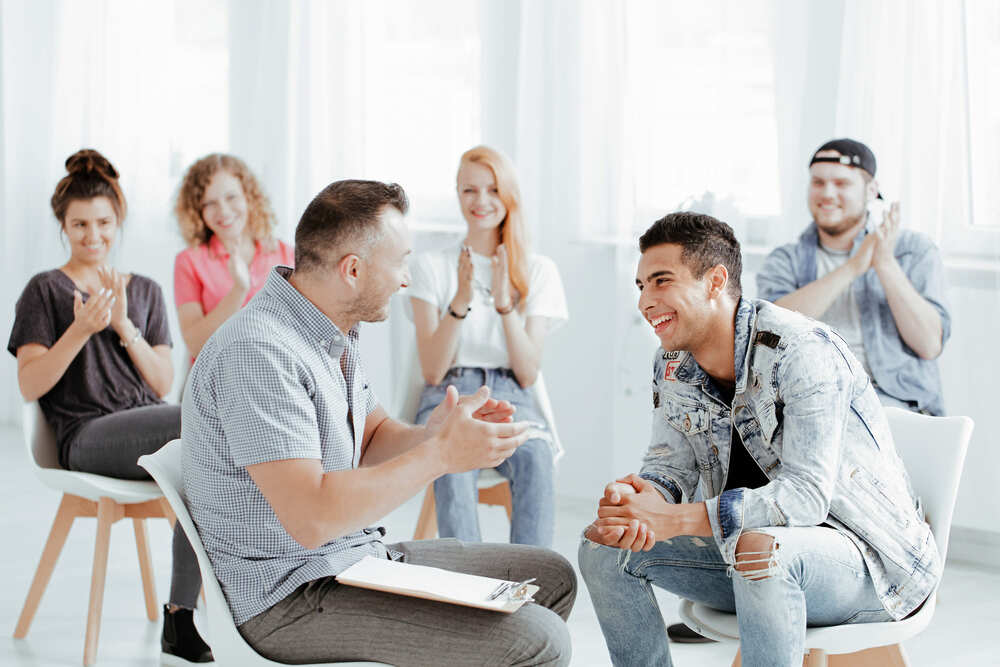
4. Support Groups
Joining a support group can provide a sense of community and understanding for those struggling with mental illness. Support groups offer a safe space to share experiences, learn coping strategies, and connect with others who are on a similar journey.
5. Complementary and Alternative Therapies
Some individuals may find relief through complementary and alternative treatments for mental illness, such as:
- Acupuncture
- Massage therapy
- Art or music therapy
- Herbal remedies
However, it’s crucial to consult with a mental health professional before incorporating these therapies into a treatment plan, as they may interact with other treatments or have potential side effects.
Overcoming Barriers to Treatment
Despite the availability of effective mental illness treatments, many people with mental illness face barriers to accessing care. Some common obstacles include:
- Stigma and discrimination
- Lack of awareness about mental health resources
- Financial constraints
- Limited access to qualified mental health professionals
- Cultural or linguistic barriers
To overcome these barriers, it’s essential to promote mental health literacy, advocate for increased funding and accessibility of services, and work towards creating a more inclusive and supportive society for those with mental illness.
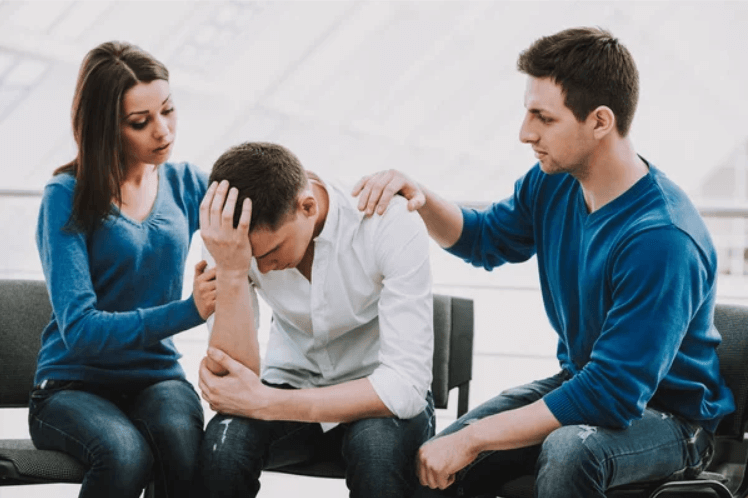
The Role of Family and Friends
Family and friends play a vital role in supporting individuals with mental illness. Some ways to provide support include:
- Educating oneself about the specific condition
- Offering a listening ear and emotional support
- Encouraging treatment adherence
- Helping with practical tasks and responsibilities
- Practicing self-care to avoid caregiver burnout
Remember, supporting a loved one with mental illness can be challenging, and it’s important to seek help for oneself when needed.
Strategies for Coping with Mental Illness

In addition to seeking professional help and support from loved ones, there are several strategies individuals can employ to cope with mental illness:
1. Develop a Routine
Establishing and maintaining a daily routine can provide structure and stability, which can be particularly beneficial for those struggling with mental health issues. This may include:
- Consistent sleep and wake times
- Regular meal times
- Scheduled activities and hobbies
- Time for self-care and relaxation
2. Practice Mindfulness
Mindfulness involves being present in the moment and observing one’s thoughts and feelings without judgment. Some ways to practice mindfulness include:
- Meditation
- Deep breathing exercises
- Body scans
- Mindful movement, such as yoga or tai chi
3. Challenge Negative Thoughts
Negative thought patterns can perpetuate mental health issues. Learning to identify and challenge these thoughts can be a powerful tool in managing mental illness. Some strategies include:
- Cognitive restructuring
- Thought-stopping techniques
- Positive self-talk
- Gratitude journaling
4. Engage in Meaningful Activities
Participating in activities that provide a sense of purpose, accomplishment, or enjoyment can boost mood and self-esteem. Some examples include:
- Volunteering
- Learning a new skill
- Pursuing a hobby
- Spending time in nature
5. Prioritize Self-Care
Self-care is essential for maintaining mental well-being. Some self-care practices include:
- Engaging in relaxation techniques
- Taking breaks when needed
- Nourishing the body with healthy food
- Staying hydrated
- Getting regular exercise