In today’s fast-paced world, mental health concerns have become increasingly prevalent. Whether it’s dealing with anxiety, depression, stress, or more severe conditions like bipolar disorder or schizophrenia, mental health issues affect millions of people globally. Thankfully, there are various mental health treatment approaches available that can help individuals manage their conditions, lead fulfilling lives, and regain a sense of balance. The three main categories of mental health treatment are therapy, medication, and holistic approaches. Each offers unique benefits and challenges, and sometimes, a combination of these options works best for individuals depending on their specific needs.
Therapy: The Power of Talking
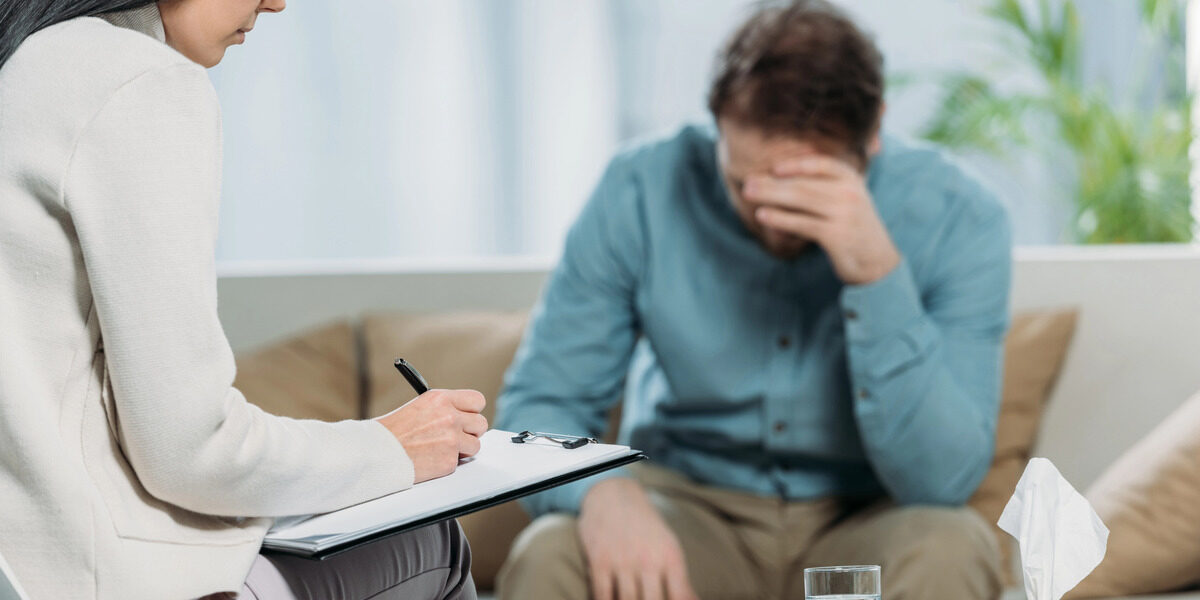
Therapy, often referred to as psychotherapy or counseling, is one of the most widely used and effective forms of mental health treatment. It involves speaking with a trained mental health professional about your feelings, thoughts, and behaviors. There are several types of therapy, each with its own approach and methodology, designed to address various mental health concerns.
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT)
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) is one of the most researched and widely used forms of therapy. Its core principle is that our thoughts, feelings, and behaviors are interconnected. By changing negative thought patterns, you can influence your emotions and actions, ultimately leading to a more positive state of mind. CBT is particularly effective for anxiety, depression, and obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD).
Dialectical Behavior Therapy (DBT)
Originally developed for individuals with borderline personality disorder, Dialectical Behavior Therapy (DBT) has since been adapted to treat a wide range of conditions, including mood disorders, suicidal behavior, and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). DBT focuses on teaching coping skills to manage emotions, tolerate distress, and improve relationships.
Psychodynamic Therapy
Psychodynamic therapy is rooted in the theories of Freud and focuses on uncovering unconscious patterns and emotions that may be influencing present-day behavior. This type of therapy is often more long-term and involves exploring past experiences, particularly those from childhood, to gain insights into current psychological challenges.
Humanistic Therapy
Humanistic therapy, including approaches like Gestalt therapy and person-centered therapy, is centered on the belief that individuals are inherently good and capable of achieving personal growth. The therapist offers a non-judgmental, empathetic environment where the client can explore their feelings and develop a stronger sense of self-worth. It’s particularly helpful for people dealing with self-esteem issues or those seeking personal fulfillment.
Family and Group Therapy
Family therapy involves the participation of family members in the therapeutic process, helping to resolve conflicts and improve communication within the family unit. Group therapy, on the other hand, involves several individuals working through their issues together with the guidance of a therapist. Both forms of therapy offer unique benefits, such as providing support from others who may share similar experiences or struggles.

Medication: Chemical Intervention for the Brain
While therapy is highly effective for many, some mental health conditions may require medication to regulate brain chemistry. Mental health medications are prescribed by psychiatrists or other medical professionals and can be incredibly helpful in treating conditions like depression, anxiety, bipolar disorder, schizophrenia, and more.
Antidepressants
Antidepressants are commonly used to treat depression, anxiety disorders, and sometimes even PTSD or OCD. There are several types of antidepressants, including:
- Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs): These increase the levels of serotonin in the brain, which can help improve mood. Common SSRIs include Prozac, Zoloft, and Lexapro.
- Serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs): Similar to SSRIs, SNRIs boost both serotonin and norepinephrine levels in the brain. Examples include Effexor and Cymbalta.
- Tricyclic antidepressants (TCAs): An older class of antidepressants that can be effective but often have more side effects than SSRIs and SNRIs.
Anti-Anxiety Medications
Anxiety disorders are commonly treated with medications such as:
- Benzodiazepines: These are fast-acting medications that can provide relief from acute anxiety or panic attacks. However, they carry a risk of dependence and are typically prescribed for short-term use. Common examples include Xanax and Valium.
- Buspirone: This is a non-benzodiazepine option for anxiety treatment. It has a lower risk of dependency but may take longer to become effective.
Mood Stabilizers
Mood stabilizers, such as lithium or certain anticonvulsant medications, are often used to treat bipolar disorder. They help regulate the extreme highs (mania) and lows (depression) associated with the condition, preventing mood swings and promoting stability.
Antipsychotics
Antipsychotic medications are prescribed for individuals experiencing psychosis, which can occur in conditions like schizophrenia or bipolar disorder. These medications help manage symptoms such as hallucinations, delusions, and severe mood swings. Antipsychotics can be divided into two categories:
- Typical antipsychotics: These are older drugs, like Haloperidol, that primarily treat positive symptoms (hallucinations and delusions).
- Atypical antipsychotics: Newer medications, like Abilify or Seroquel, which treat both positive and negative symptoms (social withdrawal, lack of motivation).
Stimulants
Stimulants, such as Adderall or Ritalin, are often prescribed for Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD). These medications help improve focus and reduce impulsive behavior in individuals diagnosed with the condition.
While medications can be life-saving and essential for many, they often come with side effects that need to be managed. It’s important to work closely with a healthcare provider to find the right medication and dosage.
Holistic Approaches: Treating the Whole Person
In addition to traditional therapy and medication, many people are exploring holistic or alternative treatments to support their mental health. Holistic approaches aim to treat the whole person—mind, body, and spirit—rather than just addressing symptoms. These treatments often focus on lifestyle changes, self-care, and natural remedies.
Mindfulness and Meditation
Mindfulness and meditation practices are designed to help individuals stay present and cultivate a sense of calm. By focusing on breathing and being aware of one’s thoughts without judgment, mindfulness can reduce stress and anxiety. Meditation, practiced regularly, can improve emotional regulation, increase focus, and even reduce symptoms of depression.
Exercise and Physical Activity
Exercise is not only beneficial for physical health but also has significant positive effects on mental health. Regular physical activity releases endorphins, which are chemicals in the brain that act as natural mood lifters. Exercise can reduce symptoms of anxiety, depression, and stress, and improve sleep patterns.
Nutrition and Diet
There is growing evidence that diet plays a crucial role in mental health. A diet rich in whole foods, such as fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and healthy fats, can support brain function and emotional well-being. Certain nutrients, like omega-3 fatty acids, found in fish, or probiotics, found in fermented foods, may have positive effects on mental health. Conversely, diets high in sugar, processed foods, and unhealthy fats can contribute to mood instability and exacerbate mental health conditions.
Herbal Remedies and Supplements
Some individuals turn to herbal remedies or dietary supplements to support their mental health. For example, St. John’s Wort is often used to treat mild to moderate depression, while valerian root and chamomile are known for their calming effects and are sometimes used to ease anxiety. It’s crucial, however, to consult a healthcare provider before starting any herbal supplements, as they can interact with medications and cause unwanted side effects.
Yoga and Tai Chi
Yoga and Tai Chi combine physical postures, breathing exercises, and meditation. These practices have been shown to reduce stress, improve mood, and enhance emotional resilience. The combination of physical movement with mindful focus can help individuals manage anxiety, depression, and chronic stress.
Acupuncture
Acupuncture, a traditional Chinese medicine practice, involves inserting thin needles into specific points on the body to balance energy flow. Some studies suggest that acupuncture may help reduce symptoms of anxiety and depression by triggering the release of neurotransmitters and endorphins.
Choosing the Right Approach
With so many treatment options available, it can be overwhelming to decide what’s best for you or your loved one. While therapy and medication are well-established options with strong clinical backing, holistic approaches can also provide complementary support. Often, a combination of these treatments is the most effective approach. For example, someone with severe depression may benefit from both medication to stabilize their mood and therapy to work through underlying issues, while also incorporating mindfulness, exercise, and healthy eating to improve overall well-being.
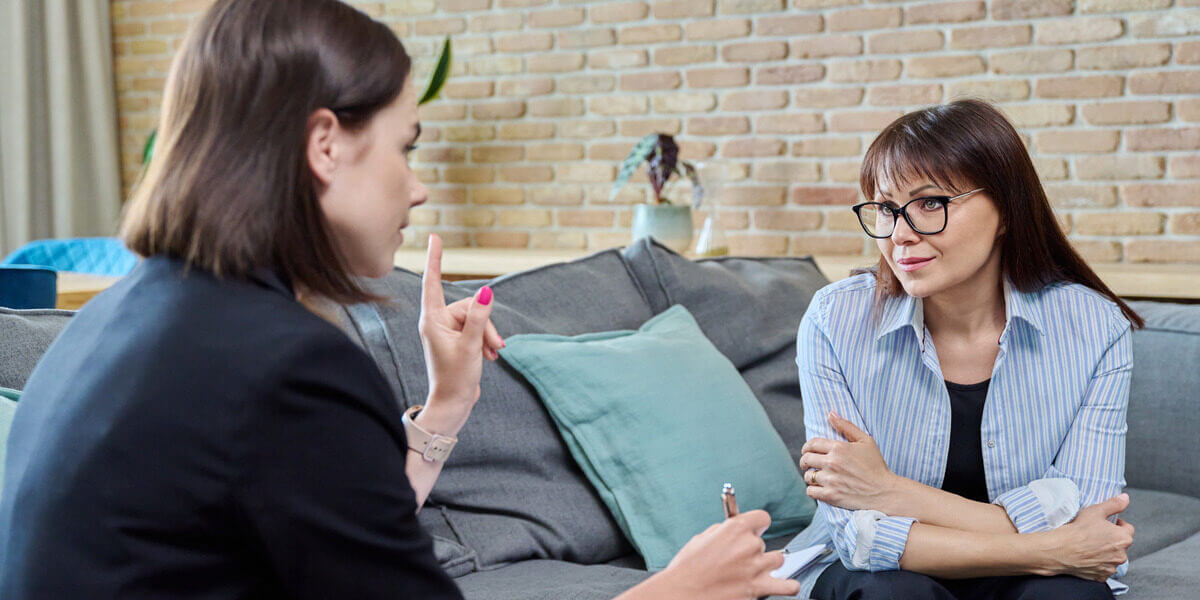
The Importance of Seeking Professional Help
Mental health is a deeply personal and complex issue, and there is no one-size-fits-all solution. While this guide provides an overview of the different types of treatment available, it is important to consult with a mental health treatment specialist to determine the most appropriate approach for your unique needs. The professionals of Aspire Frisco can help you navigate the options, develop a personalized treatment plan, and provide ongoing support throughout your mental health journey. Whether you’re considering therapy, medication, holistic approaches, or a combination of all three, reaching out for help is the first and most crucial step toward recovery and improved well-being.